
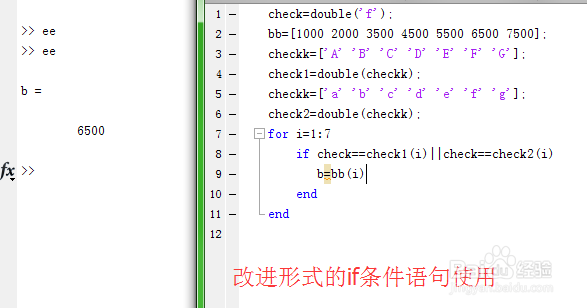
So the use of ‘if’, ‘else’ and ‘elseif’ in Matlab is veyr simple like this. Unlike ‘if’ and ‘else’, you can add numerous of conditions like above example in Matlab. Probably, you understand the logic of ‘elseif’ command above. Take a look at the very basic example below. You can add codes beneath the ‘else’ code, for the situation where teh condition for ‘if’ is not valid or false in programming logic. If this condition is valid or true in programming logic, the statement or code inside the ‘if’ will work.Īlso you can add ‘else’ between the ‘if’ and ‘end’ codes in Matlab. The Use Of ‘else’ In ‘if’ CodesĪs we stated above, ‘if’ code gives a condition to work the operation inside it. For example, if the value of ‘x’ equals to 4, the first multiplication and divison operation will be done, but the internal ‘if’ operation will not.Īccording to the program, check the new values of ‘multi’ and ‘div’ at command window above in Matlab.Įvery ‘if’ is closed with ‘end’ as you see above example. We added another ‘if’ for multiplication, inside the external ‘if’, the condition for this if is, ‘if x smaller than 3’.
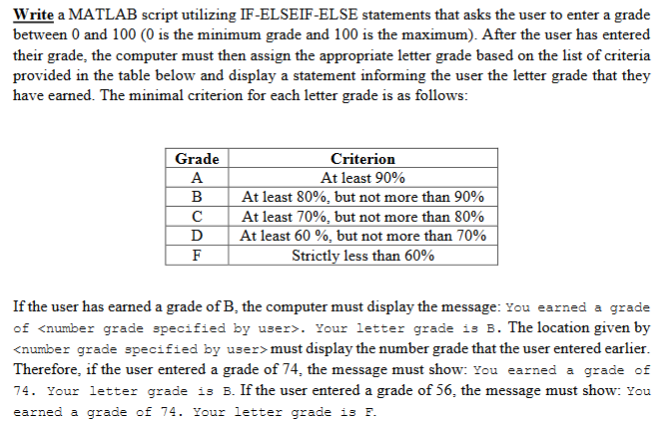
If x5’, which means if the value of ‘x’ is bigger than 5, the statement or code inside this if will work. With these logical operators, you can create your queries for different conditions.Īs you know the meaning of ‘if’ in English Language, ‘if’ is used to obtain basic logical conditions. When you use these logical queries in Matlab, you need to generally use logical operators in Matlab. How To Use ‘if’, ‘else’ and ‘elseif’ Codes In MatLab? In here, we explain the use of if, else and elseif queries in Matlab with very basic examples below. These logic statements are used in lots of codes to obtain queries for different conditions for different variables. In each case, the output is biased by +2.If, Elseif and Else statements are important in such programming languages along with MatLab. When the pulse is off, the output is the clipped version of the sine wave. When the pulse is on, the output is the absolute value of the sine wave. The scope shows the sine wave input, the triggering pulse input, and the merged and biased output. The outputs of the two subsystems are never active at the same time and are merged into one signal with a Saturation block. If the input to the If block is not positive, as specified by the else condition, then the If Action Subystem Saturation between -0.75 and 0.75 is activated, which outputs a clipped version of the sine wave signal using a Saturation block. If the input is positive, as specified by the if condition, then the If Action Subsytem Abs is activated, which outputs the absolute value of the sine wave input signal. It is designed to illustrate the similarity between the If Action Subsystem block and the Enabled Subsystem block.Ī pulse generator is connected to an If block, which compares the input to zero. This example shows the effect of feeding a sine wave into If Action Subsystem blocks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
